
Here's one reason people hate this economy, despite low unemployment: A return of the misery index
The simple answer is inflation, as measured by the consumer price index, which is showing the fastest rate of price increases in nearly 40 years. To see how much economic pain that is causing, it's useful to look at another economic measure from that earlier era -- the misery index.
The misery index was created by Arthur Okun, a top economic adviser to President Lyndon Johnson. It became more widely known in the 1970s and early 1980s. It adds together two measures of economic pain -- the unemployment rate and the CPI's measure of inflation -- to create a single number. The lower the number, the happier consumers -- and voters -- were likely to be. The higher, the more unhappy.
Right now the measure stands at a level Americans haven't consistently seen since the Great Recession and the years that followed.
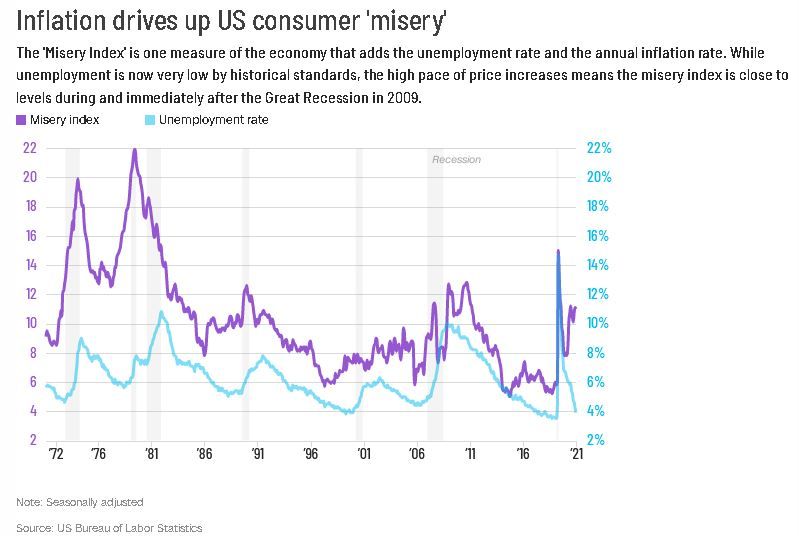
The misery index has been in double digits since April, standing at 11 or higher since December. The next CPI report is Thursday.
That's where it also stood in late 2008 as the Great Recession took hold, and in late 2009, when unemployment peaked at 10.2%. That was a mirror of today's conditions -- high unemployment in a badly wounded labor market, but coupled with very low, even negative, inflation.
The misery index returned to double-digit territory in 2011 and early 2012 when unemployment remained stubbornly high and prices temporarily surged -- at about half the current rate. The misery index was briefly higher than its current level during the brief spike in unemployment in the early months of the pandemic.
Still, the misery index was significantly higher at its peak in the 1970s and early 1980s, when the economy was struggling with much higher inflation and unemployment.
It was in the teens -- or higher -- for about a decade from late 1973 to mid-1983, climbing above 20 for most of 1980.
A good 'rule of thumb'
Economists agree the misery index is not a particularly sophisticated measure. Other economists since the 1980s have come up with more precise measures.
But, in its original form, the misery index is useful nonetheless.
"It's short-hand, it's a rule of thumb," said David Wessel, director of the Hutchins Center on Fiscal & Monetary Policy at Brookings Institution. "The average person can understand it. You don't need a PhD in Economics to add together two numbers."
The reason people are upset about high prices -- beyond the squeeze on their budgets -- is that it's a factor that they confront on a continuing basis. Even during periods of high unemployment, more than 85% of Americans will keep working. But nearly 100% of people are paying higher prices during periods of high inflation.
"High unemployment and inflation, either one is upsetting," said Wessel. "If you're out of work you're more worried about unemployment. If you have a job, you're more worried about inflation."
Economic worries despite low unemployment
The labor market is exceptionally strong right now. There are more job openings than there are job seekers. That's allowed Americans able to quit jobs they don't like, often to take better jobs. Wages are rising as a result. The latest consumer confidence report from The Conference Board, an economics research firm, found 55% said jobs were plentiful, five times as much as those who said jobs are hard to get.
The Conference Board's survey found Americans generally positive about the state of the economy, especially compared to during the depths of the Great Recession.
But other surveys cast a more negative outlook.
The most recent CNN poll on the economy in December found three-quarters of those surveyed say they are worried about the state of the economy in their own community, and 63% say the nation's economy is in poor shape. It also found 80% expressing concern about inflation and 54% disapproving of the way President Joe Biden's performance dealing with the economy.
Gallup's poll in early January found only 23% saying the economy is in good or excellent shape, while 37% say it is in poor shape, down only slightly from the 42% who said it was in poor shape in December. That represents the highest percentage of people who believe the economy is in poor shape since 2012.
In some ways, the misery index does a better job of predicting political reaction to the economy than explaining the economic reality, noted Steve Hanke, professor of applied economics at the Johns Hopkins University and a member of President Ronald Reagan's Council of Economic Advisers.
"It's not a pain gauge. It's a polling gauge," said Hanke, who has come up with a revised version of the index to compare economies in different countries.
"That was the whole purpose of the thing. The bottom line is the original one gives politicians what they need to know."
A misery index close to these readings is typically bad news for political leaders. Presidents Gerald Ford, Jimmy Carter and George H.W. Bush all became one-term presidents with a misery index in double-digits in the run-up to the election.
The good news for Biden is there is time for the economy to improve in the eyes of voters. Many economists believe current prices are a temporary condition caused by the pandemic and that the inflation rate could come down between now and the 2022 midterm elections, let alone the next presidential election in 2024. Hanke said what is most important for politicians is that people have a sense that things are improving -- that's more important than the misery index reading itself.
For proof, the misery index stood near the current reading in the fall of 1984, but that was down nearly 50% from four years earlier. It allowed Reagan to base his campaign on an improving economy, with his ads proclaiming "It's morning in America."
But if economists are wrong and inflation remains persistent, or if efforts to curb it cause a strong labor market to sour and unemployment to rise, history suggests it will be very bad news for Biden and Democrats.
"It would be inconvenient for Biden if we were running the election now," said Wessel.











