
Will a Russian diamond ban be effective?
Countries in the G7 bloc also want to be able to trace the gemstones to block Russian exports as they try to limit cash flowing into Russia's war chest.
But how effective will these schemes be, and could there be unintended consequences?
How important are Russian diamond exports?
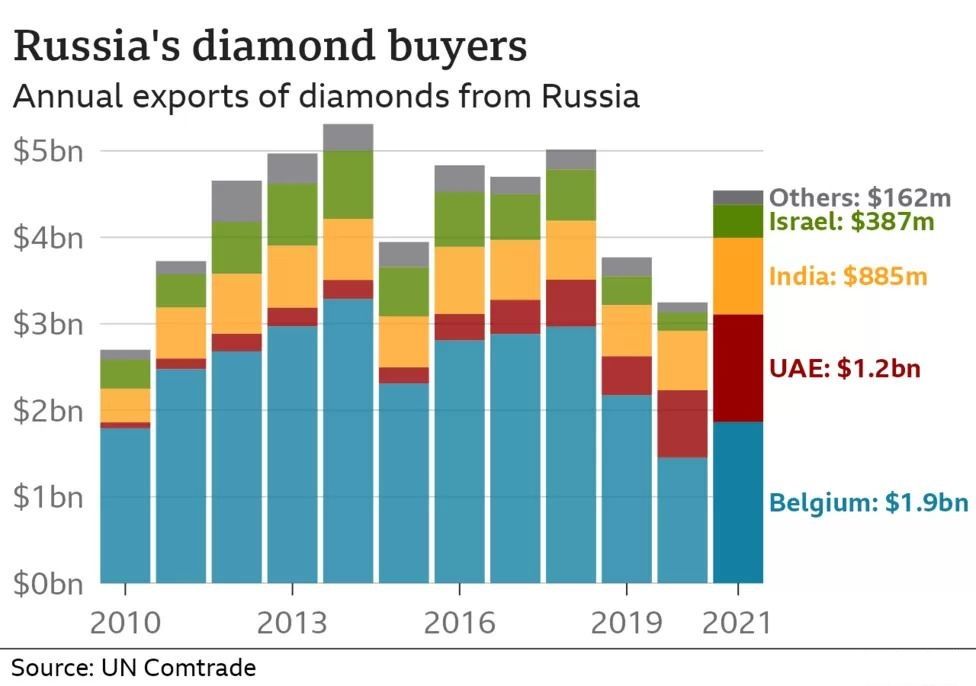
Russia's diamond trade, worth about $4bn (£3.2bn) per year, makes up a small proportion of its overall exports.
Before the invasion of Ukraine, Russia's total exports reached $489.8bn in 2021, according to the central bank, with oil and gas making up $240.7bn of that.
Nevertheless, Russia is the world's biggest diamond exporter by volume, followed by African countries.
A state-owned company called Alrosa dominates Russian diamond mining - and it mined almost a third of the world's diamonds in 2021.
Profits from Alrosa do flow into the Kremlin war chest, according to Hans Merket, a researcher with the International Peace Information Service - but it is nowhere near as important as oil and gas.
Why does the G7 want to track Russian diamonds?
Western countries want to cut off this revenue stream as part of efforts to hamper Russia's war.
However, the world's diamond trade is complex, and lacks transparency.
Diamonds can change hands 20 to 30 times between mine and market, Mr Merket said.
Typically the gemstones pass through the main global hubs of Antwerp, Dubai, Mumbai and Ramat Gan, which is near Tel Aviv.
Traders grade the stones for carat (weight), colour, clarity and cut - with different traders looking for different attributes.
They then take the remaining gemstones, mix them up, and sell them on - and the process is repeated.
Traders and firms jealously guard where they source their diamonds - it's their "secret sauce", according to Tobias Kormind, managing director of online jeweller 77 Diamonds.
But the major industry players could restrict the trade of Russian diamonds if they pulled together, he said.
How could the flow of Russian diamonds be restricted?
The US has already brought in sanctions to try to ban Russian diamond exports.
However, there is a "massive loophole" here, Mr Kormind said.
The restrictions apply to rough diamonds - but once they have been cut and polished, the country of origin no longer matters.
People in G7 countries buy about 70% of the world's diamonds - so a G7 ban could have an effect, if the diamonds can be traced, Mr Merket said.
However, a G7 ban would mean diamonds are likely to flow to other markets in China and India, Mr Kormind said.
Tracing the diamonds would make restricting that flow easier.
How could diamonds be traced?
There is already a scheme to try to restrict "blood diamonds" used to fuel conflict, called the Kimberley Process, where states certify that diamonds are "conflict free".
However, this does not allow the diamonds to be traced to the country of origin.
Mr Merket said the simplest way of tracing diamonds would be to extend this process to include documentation of where the stones come from.
There are also technologies that mark stones, and one is being developed that can scan them to check their geographical origin.
What effects would a ban have?
The majority of Russian diamonds end up in India, where there is a major cutting and polishing centre in Surat.
Smaller diamond businesses in the city have already suffered, in part due to the US ban.
In Africa, local mining operations benefitted after US sanctions hit Russian exports. However, many African mining producers are not ready to feed into a traceability scheme, Mr Merket said, and could be excluded if one is brought in.
In Angola, Russia's Alrosa has a significant stake in mining, and tightening sanctions could hit local firms.
For Europe, traceability needs to be "watertight, scientific, [and] international", said Tom Neys, head of media relations at the Antwerp World Diamond Centre.
If not, Europe risks losing $40bn in trade annually to places that don't have the frameworks to deal with money laundering and terrorism, he said.
He added that UK sanctions "will have no impact on the sale of Russian diamonds" because the UK represents less than 1% of the global diamond trade.
A UK government spokesperson said it would work with key partners to help restrict the Russian diamond trade, "including through tracing technologies".











