NASA Discovers We Are in Serious Trouble
Scientists working with the James Webb and Hubble Space Telescopes have confirmed that the observed result indicating the universe's expansion rate is not uniform but varies in speed cannot be attributed to measurement errors.
Astronomers utilized the James Webb and Hubble telescopes to confirm one of theoretical physics' most troubling puzzles: the universe expands at an incredibly different pace depending on the point of observation.
THE NON-UNIFORM EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE IS NOT A MEASUREMENT ERROR, WE MISUNDERSTOOD THE COSMOS
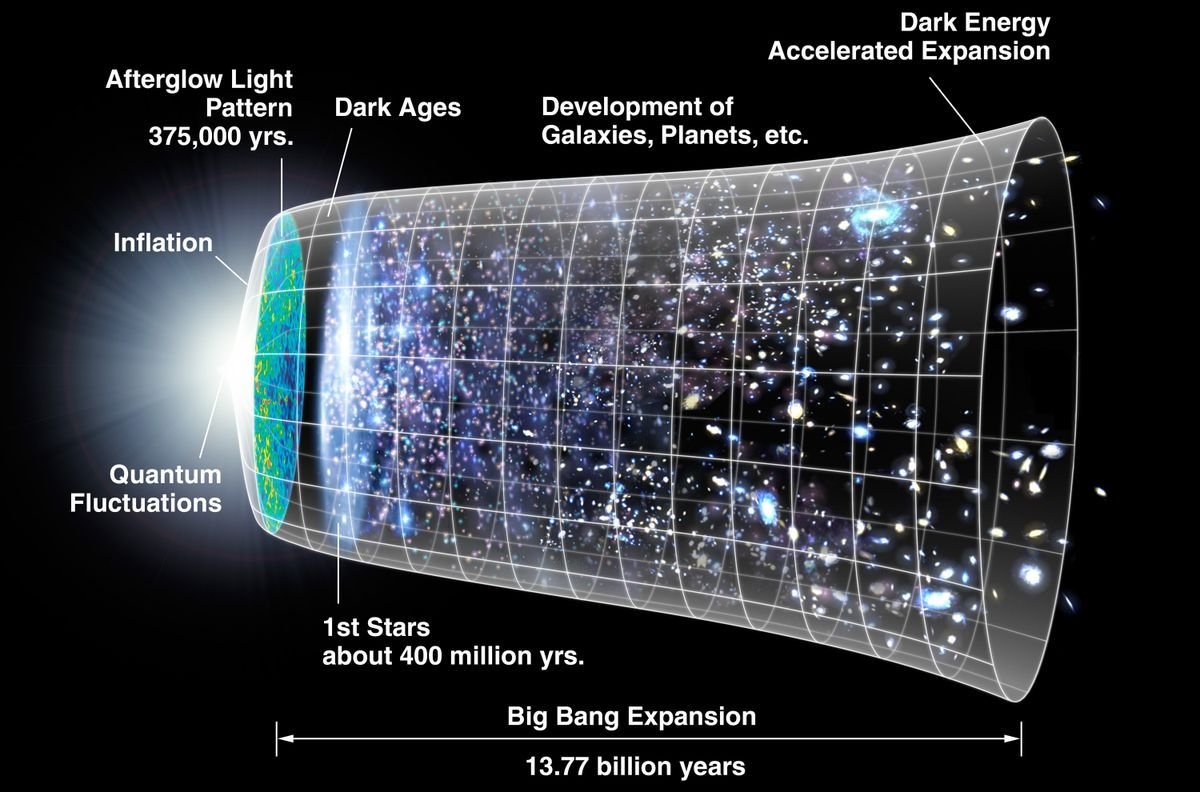
This issue, known as the Hubble tension, has the potential to change or even completely overturn the current cosmological model. Initially uncovered through measurements by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2019, this unexplainable anomaly was once again verified to be real by even more accurate measurements taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in 2023. A thorough triple-check of observational data from the two telescopes has definitively ruled out the possibility of measurement errors. A study published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters on February 6 suggests that there may be a significant problem with understanding the universe.
Dismissing measurement errors, we are left with the genuine and exciting possibility that we misunderstood the universe, stated Adam Riess, lead author of the study and a professor of physics and astronomy at Johns Hopkins University. It is worth noting that Riess, along with fellow researchers Samuel Perlmutter and Brian P. Schmidt, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011 for their work on the discovery of the universe's accelerating expansion and their contributions to the study of hypothetical dark matter. Currently, two "gold standard" methods exist for determining the so-called Hubble constant, which describes the rate of the universe’s expansion.
The first method starts with the minute fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), the universe's first light's ancient remnant, formed just 380,000 years after the Big Bang. Between 2009 and 2013, astronomers thoroughly mapped this faint microwave background field with the European Space Agency's (ESA) Planck satellite, finding the Hubble constant to be precisely 67 km/s/Mpc. The Hubble constant allows for the calculation of the so-called Hubble time, i.e., the age of the universe. Edwin P. Hubble discovered in 1929 that the spectral shift of galaxies towards the red end (Doppler effect) signifies galaxies move away from us at speeds that increase with distance.
This observation led Belgian cosmologist and theoretical physicist Georges Lemaître in 1931 to propose the hypothesis of the Big Bang or the expanding universe. According to Lemaître, by extrapolating the velocity vectors backward in time, a point when all the universe's matter was condensed into a single point from which our known world began with the Big Bang. Current knowledge places the Hubble time at approximately 13.8 billion years.
THIS IS NOT A PROBLEM, BUT RATHER A CRISIS
The second "gold standard" utilizes Cepheid variable stars to determine the Hubble constant. Cepheids, first identified within the Cepheus constellation and named after the delta Cephei star, are old stars on the brink of death that periodically pulsate in brightness. As Cepheids brighten, they pulse more slowly, allowing astronomers to measure their absolute luminosity. By comparing this luminosity to their observed brightness, astronomers can place Cepheids into a "cosmic distance ladder" to peer deeper into the universe's past. This ladder helps provide accurate values for the expansion rate through the redshift of Cepheids' spectra.
However, this is where the mystery begins. Measurements conducted by professor Riess and his team on Cepheid variables indicated the universe's expansion rate to be approximately 74 km/s/Mpc, a value incredibly higher than that measured by the Planck satellite. Regarding the variable rate of universe expansion, Nobel laureate astronomer David Gross of the California Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP) remarked at a 2019 conference:
I would call this not tension or a problem but rather a crisis.
Initially, some thought the discrepancy could be due to a measurement error caused by mixing Cepheids and other stars in the Hubble's aperture. However, in 2023, researchers using the more accurate James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) confirmed the correctness of the Hubble measurements.
To solve the problem, Riess and his colleagues built on their previous measurements and observed an additional 1,000 Cepheid variables in five galaxies about 130 million light-years away from Earth. After comparing their data with earlier measurements by the Hubble Space Telescope, they confirmed the accuracy of the obtained value for the Hubble constant. "We have now covered the full range of observations with the Hubble Space Telescope and can exclude measurement error as the cause of the Hubble tension with high confidence," said Riess. "Combining Webb and Hubble provides us with the best of both worlds. We find Hubble's measurements reliable as we climb further up the cosmic distance ladder," remarked the Nobel laureate scientist. In other words, the problem that stretches the bounds of traditional cosmology remains unanswered.
THE ACCELERATED EXPANSION COSMOLOGICAL MODEL IN QUESTION
The hypothesis of an expanding, yet finite and boundless universe was established by Albert Einstein within his general theory of relativity formulated in 1915 and published the following year. In Einstein's theory, gravity is the result of the curvature of spacetime, indicating the universe's finiteness. British Sir Arthur Eddington in 1919 provided empirical astrophysical evidence for the universe's curvature, and Edwin P. Hubble discovered the universe's expansion in 1929. A consequence of the universe's expansion is that light stretches and shifts to longer wavelengths as it passes through cosmic space, a phenomenon also responsible for the redshift observed when astronomers view increasingly distant, and thus older, galaxies.
Belgian Georges Lemaître, the first to formulate the Big Bang theory, calculated the universe's origin to be 13.8 billion years ago based on current precise measurements. However, contrary to the expectation of Einstein's gravitational model that the expansion rate should slow over time, Samuel Perlmutter, Brian P. Schmidt, and Adam Riess discovered in 1998 that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. The concept of dark energy, a hypothetical force filling the universe and causing this acceleration, was introduced as an explanation for the accelerating expansion.
Dark energy, according to cosmological literature, is a form of energy that fills the universe, exerting an antigravitational effect or negative pressure. General relativity implies that dark energy's negative pressure neutralizes gravitational attraction over large distances. Theoretical calculations suggest the mysterious dark energy comprises 74% of the known Einsteinian universe, 22% is dark matter (a type of matter undetectable by astronomical instruments, emitting no electromagnetic radiation), 3.6% is constituted by interstellar gas, and only the remaining 0.4% makes up the mass of stars and other celestial bodies.
The only problem is, despite its appealing and logical basis for explaining the universe's accelerating expansion, dark energy's existence has yet to be empirically proven. Some doubt and attribute this peculiar phenomenon to other theoretical causes. The fact that the expansion rate varies, meaning some parts of space expand faster than others, challenges the previously consensus cosmological model.
THE NON-UNIFORM EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE IS NOT A MEASUREMENT ERROR, WE MISUNDERSTOOD THE COSMOS
This issue, known as the Hubble tension, has the potential to change or even completely overturn the current cosmological model. Initially uncovered through measurements by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2019, this unexplainable anomaly was once again verified to be real by even more accurate measurements taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in 2023. A thorough triple-check of observational data from the two telescopes has definitively ruled out the possibility of measurement errors. A study published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters on February 6 suggests that there may be a significant problem with understanding the universe.
Dismissing measurement errors, we are left with the genuine and exciting possibility that we misunderstood the universe, stated Adam Riess, lead author of the study and a professor of physics and astronomy at Johns Hopkins University. It is worth noting that Riess, along with fellow researchers Samuel Perlmutter and Brian P. Schmidt, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011 for their work on the discovery of the universe's accelerating expansion and their contributions to the study of hypothetical dark matter. Currently, two "gold standard" methods exist for determining the so-called Hubble constant, which describes the rate of the universe’s expansion.
The first method starts with the minute fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), the universe's first light's ancient remnant, formed just 380,000 years after the Big Bang. Between 2009 and 2013, astronomers thoroughly mapped this faint microwave background field with the European Space Agency's (ESA) Planck satellite, finding the Hubble constant to be precisely 67 km/s/Mpc. The Hubble constant allows for the calculation of the so-called Hubble time, i.e., the age of the universe. Edwin P. Hubble discovered in 1929 that the spectral shift of galaxies towards the red end (Doppler effect) signifies galaxies move away from us at speeds that increase with distance.
This observation led Belgian cosmologist and theoretical physicist Georges Lemaître in 1931 to propose the hypothesis of the Big Bang or the expanding universe. According to Lemaître, by extrapolating the velocity vectors backward in time, a point when all the universe's matter was condensed into a single point from which our known world began with the Big Bang. Current knowledge places the Hubble time at approximately 13.8 billion years.
THIS IS NOT A PROBLEM, BUT RATHER A CRISIS
The second "gold standard" utilizes Cepheid variable stars to determine the Hubble constant. Cepheids, first identified within the Cepheus constellation and named after the delta Cephei star, are old stars on the brink of death that periodically pulsate in brightness. As Cepheids brighten, they pulse more slowly, allowing astronomers to measure their absolute luminosity. By comparing this luminosity to their observed brightness, astronomers can place Cepheids into a "cosmic distance ladder" to peer deeper into the universe's past. This ladder helps provide accurate values for the expansion rate through the redshift of Cepheids' spectra.
However, this is where the mystery begins. Measurements conducted by professor Riess and his team on Cepheid variables indicated the universe's expansion rate to be approximately 74 km/s/Mpc, a value incredibly higher than that measured by the Planck satellite. Regarding the variable rate of universe expansion, Nobel laureate astronomer David Gross of the California Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP) remarked at a 2019 conference:
I would call this not tension or a problem but rather a crisis.
Initially, some thought the discrepancy could be due to a measurement error caused by mixing Cepheids and other stars in the Hubble's aperture. However, in 2023, researchers using the more accurate James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) confirmed the correctness of the Hubble measurements.
To solve the problem, Riess and his colleagues built on their previous measurements and observed an additional 1,000 Cepheid variables in five galaxies about 130 million light-years away from Earth. After comparing their data with earlier measurements by the Hubble Space Telescope, they confirmed the accuracy of the obtained value for the Hubble constant. "We have now covered the full range of observations with the Hubble Space Telescope and can exclude measurement error as the cause of the Hubble tension with high confidence," said Riess. "Combining Webb and Hubble provides us with the best of both worlds. We find Hubble's measurements reliable as we climb further up the cosmic distance ladder," remarked the Nobel laureate scientist. In other words, the problem that stretches the bounds of traditional cosmology remains unanswered.
THE ACCELERATED EXPANSION COSMOLOGICAL MODEL IN QUESTION
The hypothesis of an expanding, yet finite and boundless universe was established by Albert Einstein within his general theory of relativity formulated in 1915 and published the following year. In Einstein's theory, gravity is the result of the curvature of spacetime, indicating the universe's finiteness. British Sir Arthur Eddington in 1919 provided empirical astrophysical evidence for the universe's curvature, and Edwin P. Hubble discovered the universe's expansion in 1929. A consequence of the universe's expansion is that light stretches and shifts to longer wavelengths as it passes through cosmic space, a phenomenon also responsible for the redshift observed when astronomers view increasingly distant, and thus older, galaxies.
Belgian Georges Lemaître, the first to formulate the Big Bang theory, calculated the universe's origin to be 13.8 billion years ago based on current precise measurements. However, contrary to the expectation of Einstein's gravitational model that the expansion rate should slow over time, Samuel Perlmutter, Brian P. Schmidt, and Adam Riess discovered in 1998 that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. The concept of dark energy, a hypothetical force filling the universe and causing this acceleration, was introduced as an explanation for the accelerating expansion.
Dark energy, according to cosmological literature, is a form of energy that fills the universe, exerting an antigravitational effect or negative pressure. General relativity implies that dark energy's negative pressure neutralizes gravitational attraction over large distances. Theoretical calculations suggest the mysterious dark energy comprises 74% of the known Einsteinian universe, 22% is dark matter (a type of matter undetectable by astronomical instruments, emitting no electromagnetic radiation), 3.6% is constituted by interstellar gas, and only the remaining 0.4% makes up the mass of stars and other celestial bodies.
The only problem is, despite its appealing and logical basis for explaining the universe's accelerating expansion, dark energy's existence has yet to be empirically proven. Some doubt and attribute this peculiar phenomenon to other theoretical causes. The fact that the expansion rate varies, meaning some parts of space expand faster than others, challenges the previously consensus cosmological model.
Translation:
Translated by AI
AI Disclaimer: An advanced artificial intelligence (AI) system generated the content of this page on its own. This innovative technology conducts extensive research from a variety of reliable sources, performs rigorous fact-checking and verification, cleans up and balances biased or manipulated content, and presents a minimal factual summary that is just enough yet essential for you to function as an informed and educated citizen. Please keep in mind, however, that this system is an evolving technology, and as a result, the article may contain accidental inaccuracies or errors. We urge you to help us improve our site by reporting any inaccuracies you find using the "Contact Us" link at the bottom of this page. Your helpful feedback helps us improve our system and deliver more precise content. When you find an article of interest here, please look for the full and extensive coverage of this topic in traditional news sources, as they are written by professional journalists that we try to support, not replace. We appreciate your understanding and assistance.