
Only 2.8 million Americans have received COVID-19 vaccines, far short of the Trump administration's goal to reach 20 million by year's end
The US is nowhere close to meeting its coronavirus vaccination goal for the end of 2020, raising concerns about how long it will take to immunize a vast majority of the American public and curb the pandemic.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration's coronavirus vaccine initiative, predicted 20 million Americans would get a coronavirus shot by year's end. Just less than 2.8 million people have received their first injections as of Wednesday morning, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the US has shipped out about 12.4 million doses.
On a call with reporters on Wednesday, Warp Speed officials acknowledged that the rollout was running behind schedule. Just an hour before the CDC provided updated vaccine data, Warp Speed officials said they didn't know how many shots had been given to date, but acknowledged that the number was short of their goal.
"We agree that number is lower than we hoped for," Moncef Slaoui, Warp Speed's chief scientific advisor, said on the press call.
The slow vaccine rollout risks delaying an end to the pandemic, and calls into question the timelines top government officials have offered up. They've said shots could be available to most adults who want them in the Spring.
At the current pace of vaccinations, it would take years for the US to immunize enough people to end the pandemic, Dr. Leana Wen, former Baltimore health commissioner, said Monday on CNN.
"For us to reach 80% herd immunity through vaccination, it will take us 10 years at a rate of 1 million vaccines a week," she said. "Or, put in a different way, if we want to get there within six months, we have to be doing 3.5 million vaccinations a day, not 1 million a week."
Dr. Nancy Messonnier, director of CDC's National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters on Wednesday that she expects the pace of vaccinations to increase after the holidays. She said some places planned for a "more measured" start to their vaccine campaigns before ramping up.
"I really expect that those numbers are going to increase fast next week," she said on a call with reporters.
The US Defense Department and Gen. Gustave Perna are leading Warp Speed's distribution plan, and states are ultimately responsible for administering the shots and deciding who gets them.
'We're playing a lot of catch-up'
In the absence of clear federal guidance, the vaccine rollout has devolved into a patchwork response that varies by state, said Dr. Marissa Levine, a public-health professor at the University of South Florida, told Business Insider.
Local health officials have been tasked with coordinating vaccination timelines while caring for sick patients. Many health departments lack the funding to hire enough staff to administer doses in large waves. Others lack the expertise to seamlessly transfer thousands of doses from local warehouses to the arms of individuals — what experts call the "last-mile" challenge.
"A plan that took the nation as a whole into consideration probably would have been a more effective way to approach it," Josh Michaud, associate director of global health policy at the nonprofit Kaiser Family Foundation, told Business Insider.
Deferring to local authorities has defined other aspects of the US pandemic response, including ramping up testing and scrambling to secure personal protective equipment. With vaccines, however, the US has had almost a year to prepare.
"It seems like we're playing a lot of catch-up, and a lot more prep work could have been done earlier on to address the many things that are leading to our patchwork rollout right now," Michaud said.
Vaccine rollout was never going to be easy
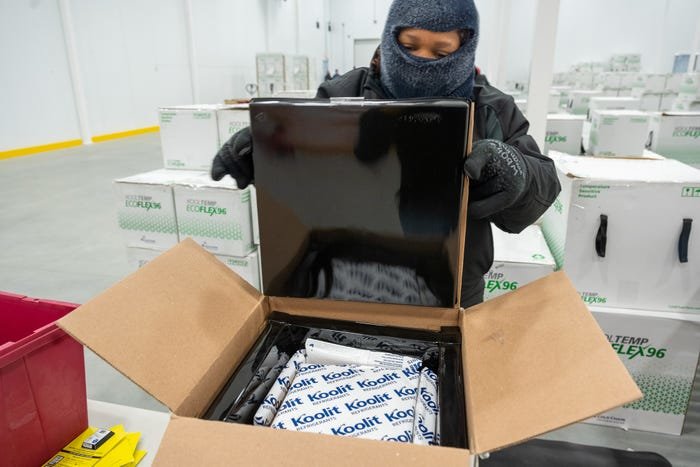

The process of delivering shots to healthcare workers and long-term care facility residents — among the first in line to be vaccinated in the US — wasn't likely to happen overnight.
Before any shipments went out, the US Food and Drug Administration took two days to assess each one for quality control, CNN reported. Then came the delicate labyrinth of unpacking each box, taking inventory of the vaccine, and preparing each dose for injection. In Pfizer's case, the vials must be stored at ultra-cold temperatures, then thawed and diluted.
That has posed a particular challenge for reaching healthcare workers at small, rural providers. Some states like Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan only started to immunize nursing home residents this week.
But public-health experts say the lagging vaccine timeline wasn't inevitable.
Levine said each state must demonstrate preparedness for public-health emergencies as part of a yearly CDC grant distributed to health departments.
"Every state has already planned for this," she said. "The question is how have they adjusted it for the specifics of COVID and these first couple of weeks and months where you have limited a vaccine are the biggest test."
If states had been given more funding or guidance early on, Levine added, they may have had an easier time preparing for a vaccine rollout. As it stands, several health authorities made questionable choices during the first few weeks of vaccine distribution.
Health officials in Williamson County, Texas, for instance, closed their offices for Christmas without administering any of the 900 doses they had recently received, the Texas Tribune's Shawn Mulcahy reported.
Some senior citizens in Lee County, Florida waited in line overnight to get access to the shot in a first-come, first-served system, wrote USA Today reporters Elizabeth Weise and Michael Braun, describing the rollout in Florida as "chaotic."
Several healthcare workers have also reported that some administrative officials are getting vaccinated ahead of those who work directly with COVID-19 patients. The vaccine rollout in Maricopa County, Arizona, was "a bit disorganized and ripe for exploitation" one local doctor told NPR, after rumors circulated that anyone with access to a certain link or phone number could get a vaccine appointment.
"We're seeing people kind of making up their own decisions without any ethical framework," Levine said. "That's a worst-case scenario, because then the people with the most power or connections are more likely to get vaccine, which is the most inequitable way to do what we need to do."
Warp Speed's shifting milestone

As recently as early December, Warp Speed leaders expressed confidence that they'd immunize 20 million Americans by the end of 2020, 30 million more in January and 50 million more in February. But the program's early struggles and slow start raise questions about these projections.
By December 19, more than two dozen states said they would be getting 30% or 40% fewer doses of Pfizer's COVID-19 shot than they initially planned for the following week. Perna, Warp Speed's chief operating officer, said the miscommunication was his fault: Supply estimates he previously gave to states turned out to be incorrect.
"I failed," Perna said at a December 19 press conference. "I am adjusting, I am fixing, and we will move forward from there."
This isn't the first time the US government has failed to meet its lofty, publicly-stated goals. When Warp Speed launched in May, the initiative aspired to deliver 300 million doses by the end of 2020.
Top federal officials have repeatedly scaled that number back. In August, Alex Azar, Secretary of Health and Human Services, lowered the year-end projection to "the high tens of millions of doses."
"They appear to be overpromising and underdelivering," Michaud said.
On Wednesday, Warp Speed's Slaoui spoke narrowly to his confidence that future estimates will hold true on manufacturing and shipping doses, but not necessarily in administering the shots.
"From an availability standpoint, there is no issue," he said. "From an administration standpoint, I concur with Gen. Perna that there is a learning curve into the system, and we're going through it."
Things could get better in the long run
Even with the slow start, the US is far ahead of all other countries in the number of administered doses, according to Bloomberg's tracker.
Like testing data, reported vaccinations lag behind the number of immunizations that have already taken place.
Both Pfizer and Moderna are confident they can deliver hundreds of millions of doses in 2021 as manufacturing is now being ramped up. Warp Speed has already struck supply deals with each drugmaker to secure hundreds of millions of doses in 2021.
"The distribution process at the national level seems to be robust," Levine said. "Unless we have huge weather issues, with the holidays behind us, hopefully we'll be able to work relatively seamlessly."
Challenges at the local level could also be eased by the recently passed coronavirus relief package, which gives states about $8 billion to help with distribution. That money "would have been helpful to have six months ago, but it's better late than never," Michaud said.
He added that states could use the funds to hire and train more workers, set up mass-administration sites, and design and launch communication campaigns to educate the public and listen to common concerns.
Joe Biden, who will become president on January 20, has set a goal of giving coronavirus vaccines to 100 million people in his first 100 days in office. That's in line with Warp Speed's timeline, but Biden has said he'll need more funding from Congress to hit the target.
Michaud said that vaccine distribution will get more challenging as it expands beyond the initial priority groups.
"I'm not seeing a uniformly concise and clear communication about how to get vaccine as it's being rolled out in a more public forum outside of, say, hospital personnel," Levine added. "People need to know how to get the vaccine, when to get the vaccine, who should get the vaccine, and then how those decisions are being made."











